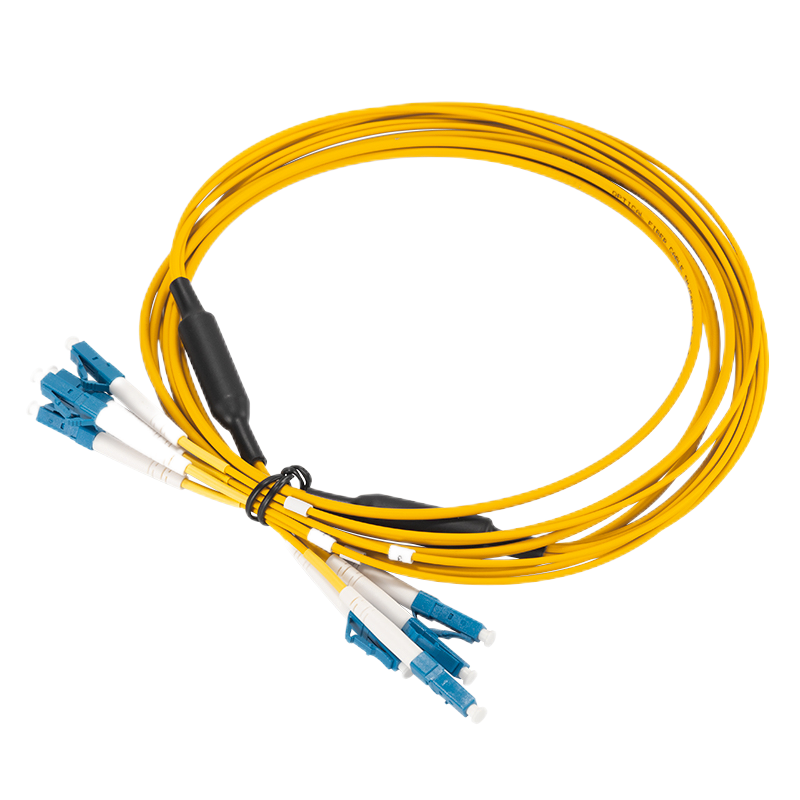
Optical Fiber Patch Cord


Fiber Connectivity
Optical Fiber Patch Cord
Fiber optic patch cords are vital in fiber optic networks, connecting devices like switches and computers. They come in single-mode for long distances and multi-mode for shorter ranges. Equipped with connectors (e.g., LC, SC), they ensure efficient light transmission. Available in various lengths and with specific jacket materials, these cords are crucial for high-speed, high-bandwidth data transmission, playing a key role in the performance and reliability of optical communication systems.
We do things differently

Types of Connectors
LC, SC, ST, FC,E2000, MPO and more

Variety Fiber Types
G.652.D, G.657, G.655 and more types

Length Customization
0.5m, 1m, 1.5m, and more as required

Waterproof outdoor type
ODVA, FullAXS, or other types commonly used in FTTA

Types of Connector
Different types of polishing, like PC, UPC and APC

Variety Cable Jacket
PVC, LSZH, OFNR, and more

High-performance
Low Insertion loss and high return loss

Jacket Color
The jacket color available to cusomization.
Optical Fiber Patch Cord
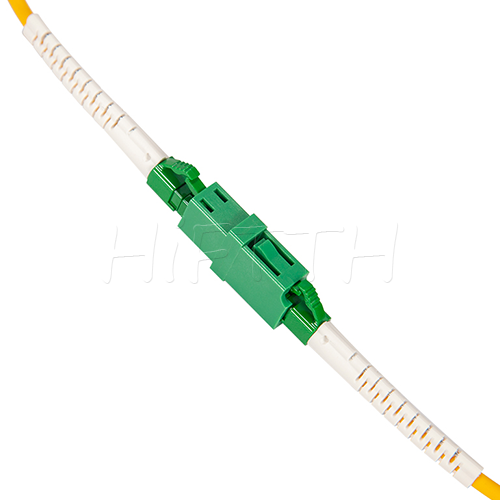
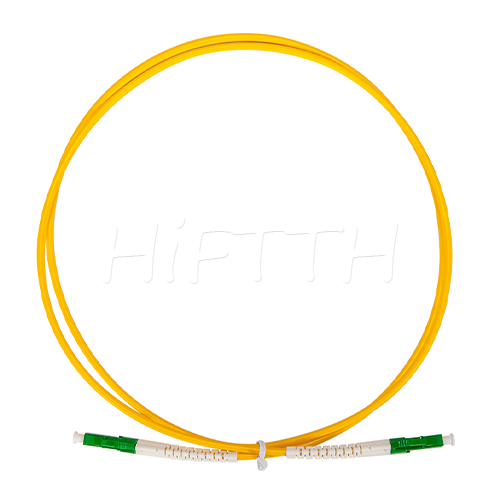
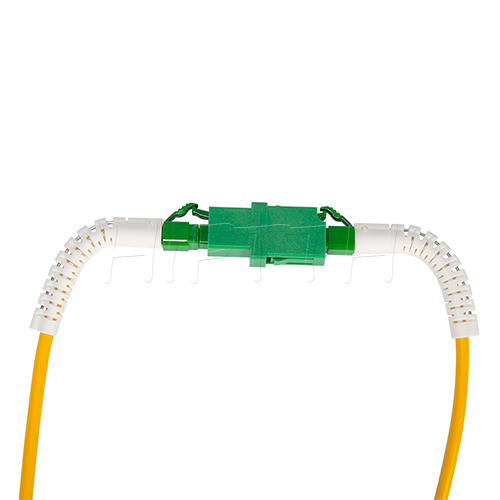
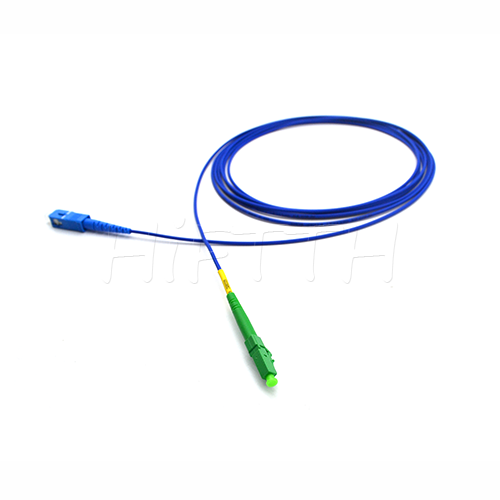
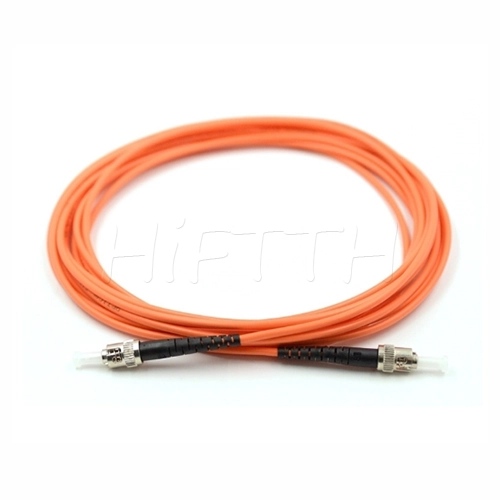
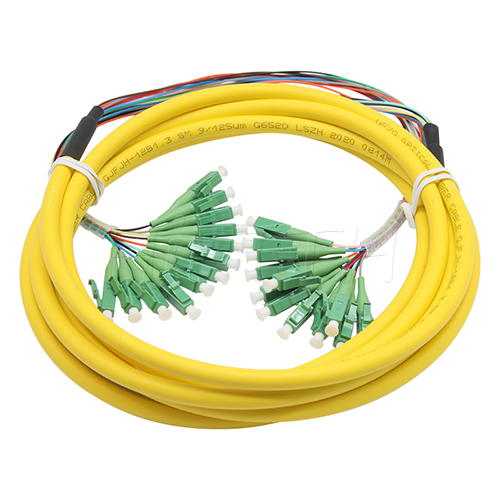
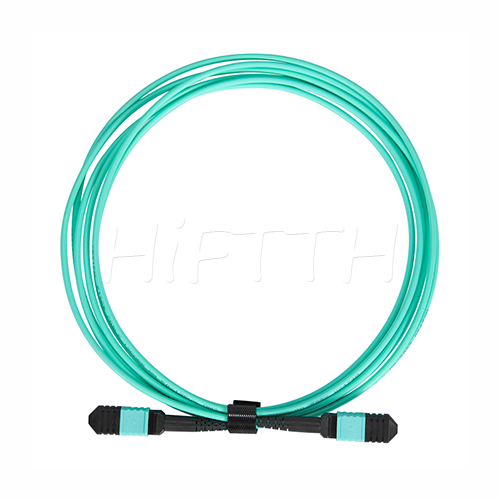
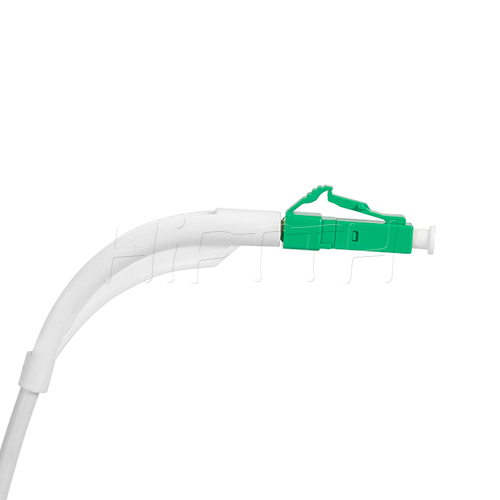
Standard (Normal) Type Optical Fiber Patch Cord
HiFTTH’s Fiber Optic Patch Cords deliver stable and high-performance connectivity with 100% quality assurance. We offer competitive pricing and flexible OEM or ODM customization to meet the specific needs of your ODN network project. Built to last, our patch cords work great in all kinds of setups.
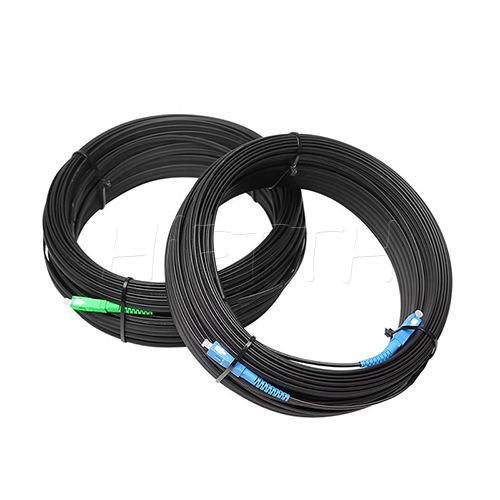




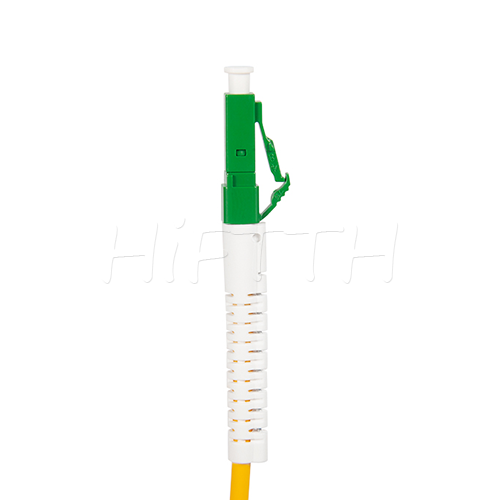










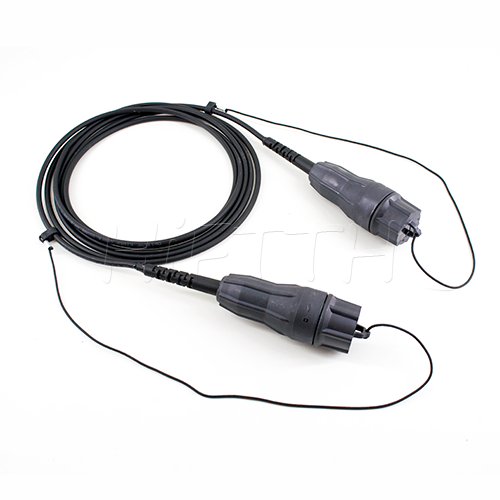
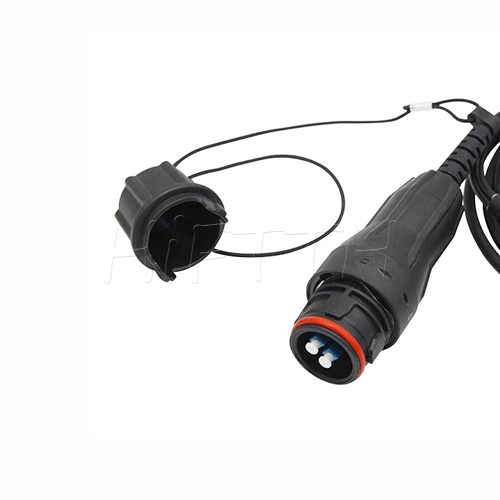
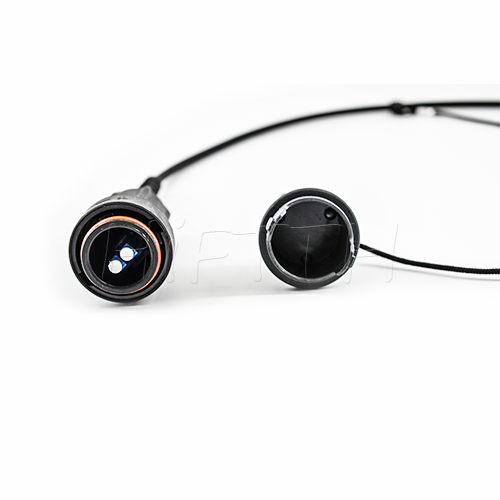
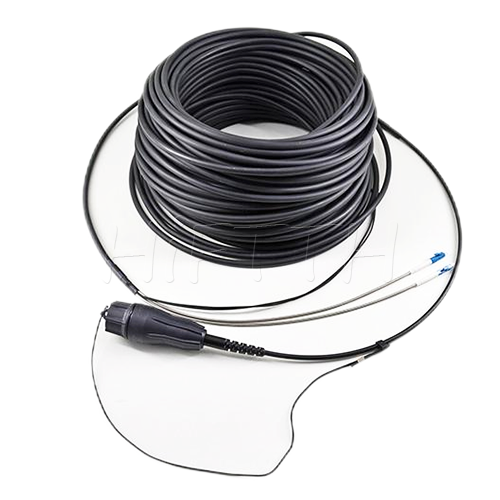
Waterproof (outdoor) Type Optical Fiber Patch Cord
HiFTTH’s Waterproof Optical Fiber Patch Cords are specially designed for FTTA applications, ensuring reliable performance in outdoor environments. With a rugged waterproof and dustproof design, they provide excellent protection against harsh weather conditions. These patch cords are available with custom lengths, connectors, and cable types to meet your exact needs. Durable and easy to install, they are the perfect solution for stable and long-lasting outdoor fiber connections.
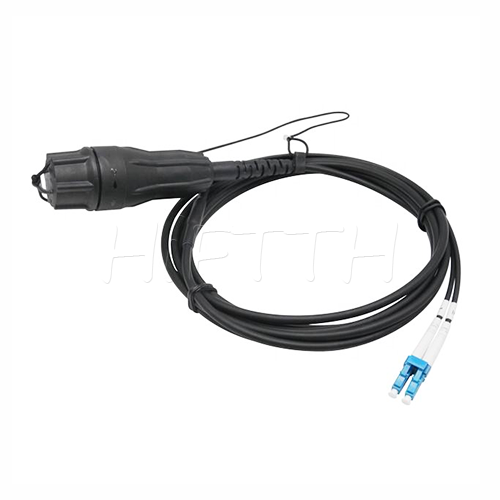
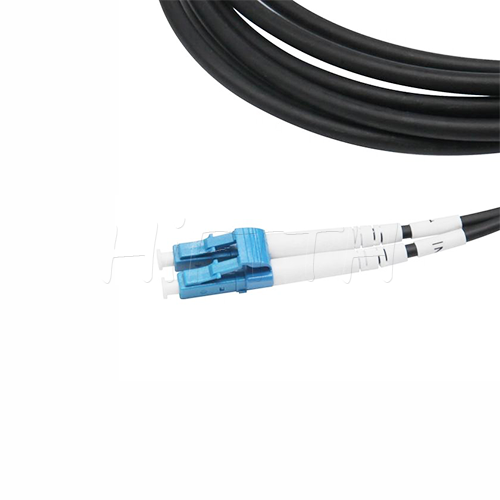
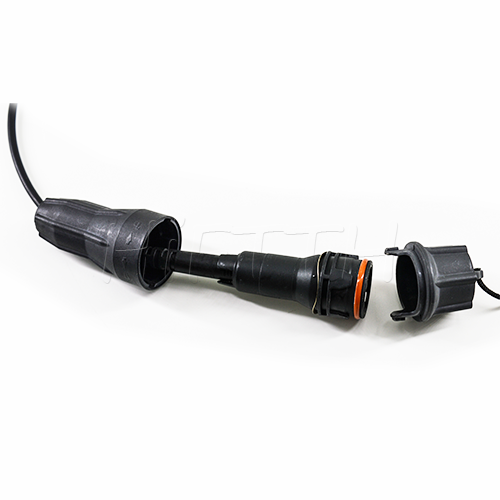
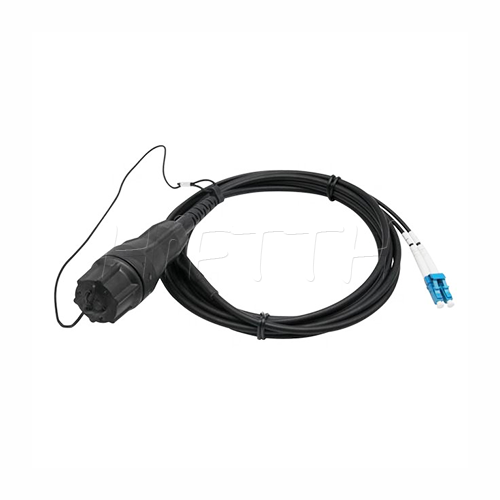









Features
Standard (Normal) Type
- 【Types of Connectors】-Common connectors on patch cords include LC, SC, ST, and FC. Each type has different characteristics and is used for different applications.
- 【Single-Mode and Multi-Mode】-Patch cords come in single-mode and multi-mode varieties. Single-mode fibers are used for long-distance transmission, while multi-mode fibers are used for shorter distances.
- 【Lengths and Colors】-They are available in various lengths to suit different needs and often come in different colors for easy identification.
- 【Jacket Material】-The jacket material can vary, offering different levels of durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
- 【Polishing Types】-The connectors can have different types of polishing (like PC, UPC, and APC) that affect the performance and suitability for different applications.
Waterproof (Outdoor) Type
- 【Robust Construction】-They are typically made with a ruggedized jacket material that is resistant to UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures. This makes them suitable for outdoor use.
- 【Waterproof Connectors】-The connectors on waterproof patch cords are specifically designed to prevent water and dust ingress. These may include standard types like LC or SC with an additional protective housing or specialized connectors like ODVA, FullAXS, or other types commonly used in FTTA.
- 【IP-Rated Protection】-These patch cords often come with IP (Ingress Protection) ratings, like IP67, indicating they are dust-tight and can withstand temporary immersion in water.
- 【Flexibility and Strength】-Despite being rugged, they are designed to be flexible enough for easy installation while also being strong enough to resist stretching, crushing, and abrasion.
- 【Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Options】-Like standard patch cords, they are available in both single-mode and multi-mode varieties, depending on the application's distance and bandwidth equirements.
Applications
Standard (Normal) Fiber Optic Patch Cord
These patch cords are widely used in data centers for high-speed data transmission. They connect various network devices like servers, switches, and storage units, facilitating efficient and fast data transfer.
Used in central offices and indoor telecommunications facilities for connecting different equipment within the network.
With the increasing demand for high-speed internet, these patch cords are also used in home fiber optic internet setups, connecting modems to routers or other home networking equipment.
Connecting devices in a local area network (LAN).
Waterproof (Outdoor) Fiber Optic Patch Cord
Used in FTTA to connect base stations to Remote Radio Units (RRUs) located on cell towers. particularly in 4G and 5G networks, where it plays a critical role in signal processing and transmission.
Ideal for use in outdoor settings where exposure to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation is a concern.
Essential for ensuring reliable data transmission in outdoor segments of telecom networks.
Military and field communication setups often use these cords due to their durability and resistance to harsh conditions.
How They Work
Standard (Normal)
Transmission of Light Signals: At one end, the patch cord is connected to a transmitter, which converts electrical signals into light signals. The light signal travels through the core of the optical fiber, which is a thin strand of glass or plastic.
Core and Cladding: The core is the inner part of the fiber where the light travels. Surrounding the core is the cladding, which reflects the light back into the core, preventing signal loss and allowing the light to travel long distances.
Connector Types:Each end of the patch cord has a connector (like LC, SC, ST, or FC) that plugs into a corresponding port on different devices (like switches, routers, servers, or optical distribution frames). The connectors align the fiber core precisely with the optical pathway in the device, ensuring efficient light signal transfer.
Signal Reception: At the receiving end, the patch cord is connected to a receiver, which converts the light signals back into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then processed by the receiving device.
Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Variations: In single-mode fibers, the core is very thin, allowing only one mode (path) of light to propagate. This type is used for long-distance transmission due to its ability to maintain the integrity of the light signal over longer distances. Multi-mode fibers have a thicker core, allowing multiple modes of light to propagate. They are used for shorter distances, as the multiple paths of light can lead to signal distortion over longer stretches.
Data Transmission: The light signals can represent digital data, which is used for communication in computer networks, telecommunication systems, and various other digital applications.
Waterproof (Outdoor)
Outdoor Installation:Waterproof patch cords are used in outdoor installations, such as connecting equipment in Fiber to the Antenna (FTTA) setups.
Connecting to Remote Radio Heads (RRH): In FTTA, these patch cords connect base station equipment to RRHs located on cell towers. They must withstand environmental challenges like rain, wind, and UV exposure.
Maintaining Signal Integrity: Despite the rugged exterior, the internal fiber optic technology ensures that the signal integrity is maintained, providing high-speed and reliable data transmission.
Handling Environmental Stress: The waterproof and ruggedized features protect the internal fibers from water damage, corrosion, and physical impacts, ensuring long-term durability and consistent performance.
How They Production
Cable Assembly
- The fibers are encased in a protective jacket. This jacket is often made of materials like PVC or LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) for protection and durability.
- Additional strengthening materials, like Kevlar or aramid yarn, may be added for extra protection and to provide tensile strength.


Connector Attachment
- On each end of the fiber, connectors (such as SC, LC, ST, or FC) are attached. This process involves stripping the fiber, cleaving it to a precise length, and then inserting it into the connector.
- The fiber is then secured inside the connector, typically with an adhesive or crimp mechanism.
Polishing the Connectors
- The connector ends are polished to ensure a high-quality connection. This is crucial for reducing insertion loss and back reflection.
- The polishing process varies depending on the connector type and may include several stages to achieve the desired end-face geometry.
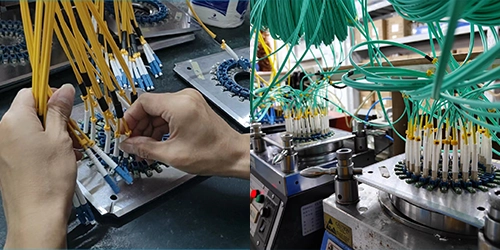

Testing for Quality and Performance
- Each patch cord undergoes testing to measure insertion loss and return loss, ensuring they meet the required specifications.
- Additional tests may include checking for mechanical and environmental durability.
- A microscopic inspection of the connector end faces is performed to ensure there are no defects that could affect performance.
Packaging
- After passing all quality checks, the patch cords are packaged. This usually involves protective caps for the connectors and secure packaging to prevent damage during transit.

Optical Fiber Patch Cord supplier
Looking for Optical Fiber Patch Cord for your Project?
Products Shows
What we supply
Optical Fiber Patch Cord
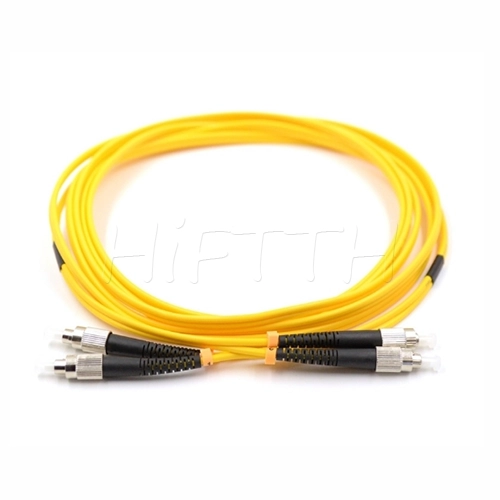
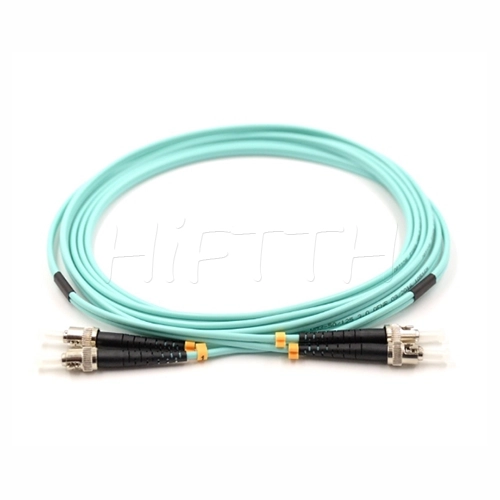
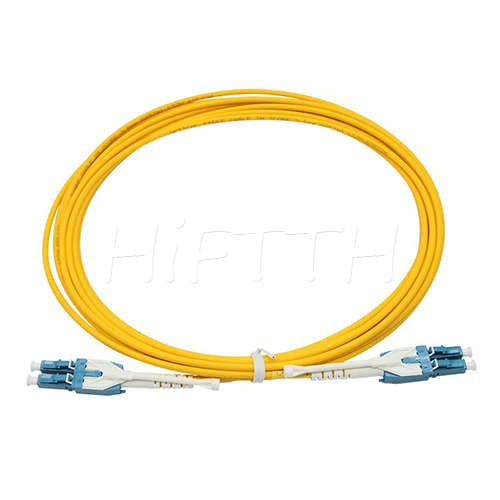
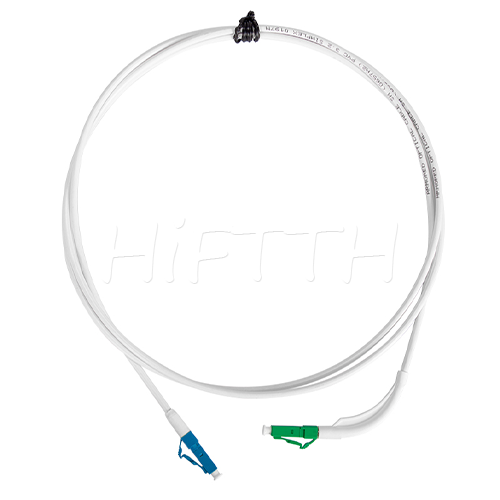
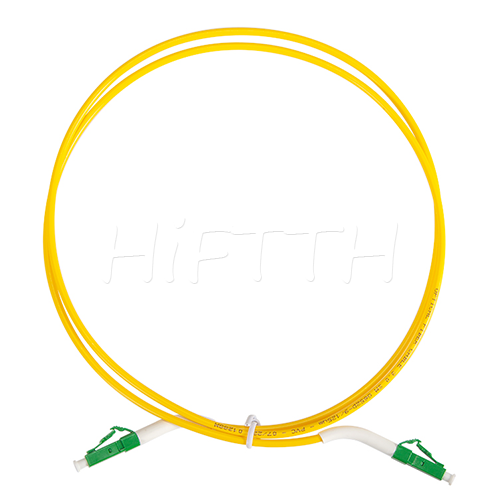
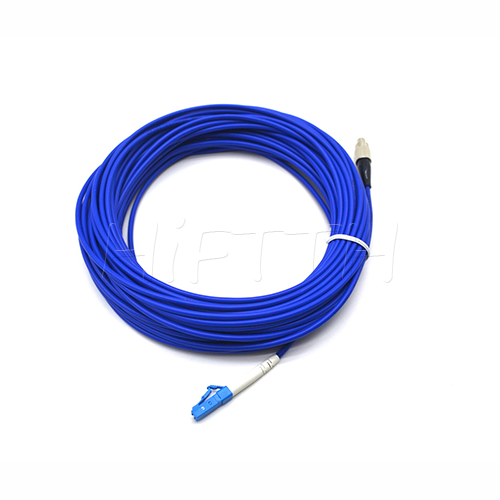
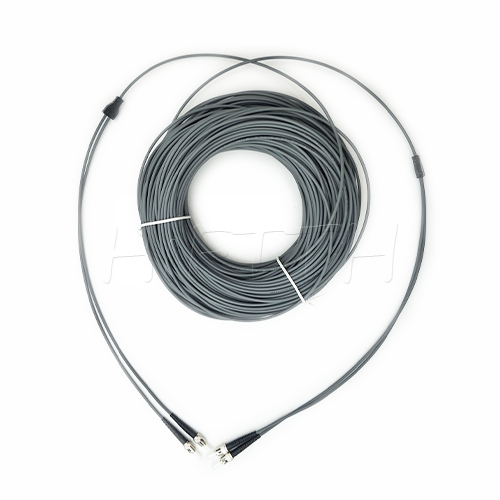
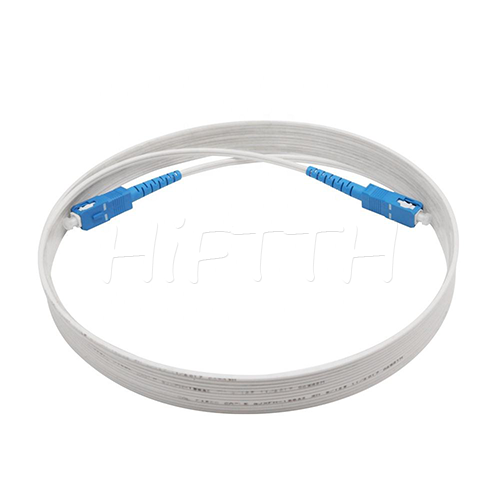
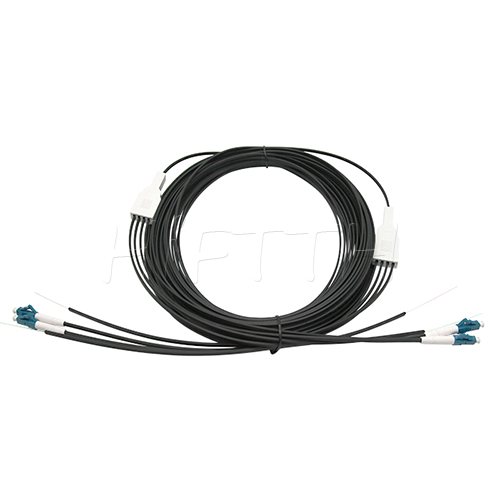
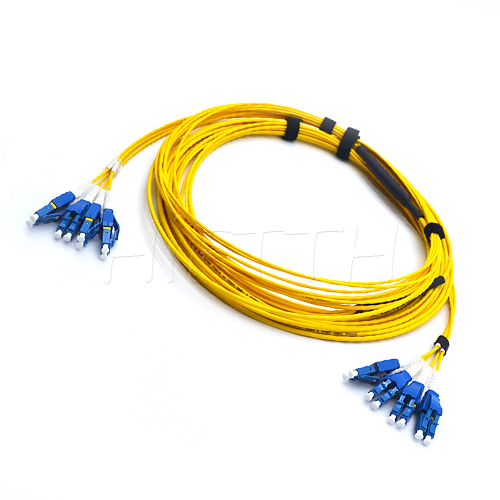
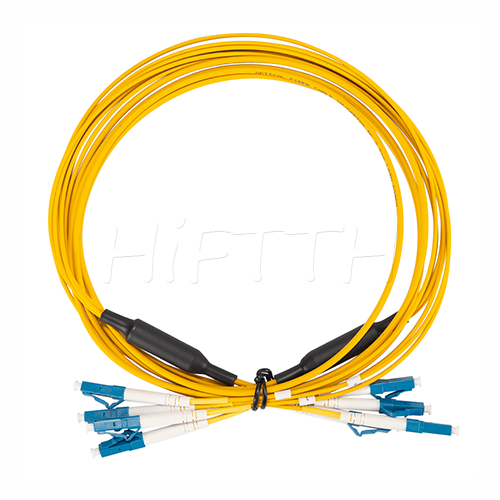
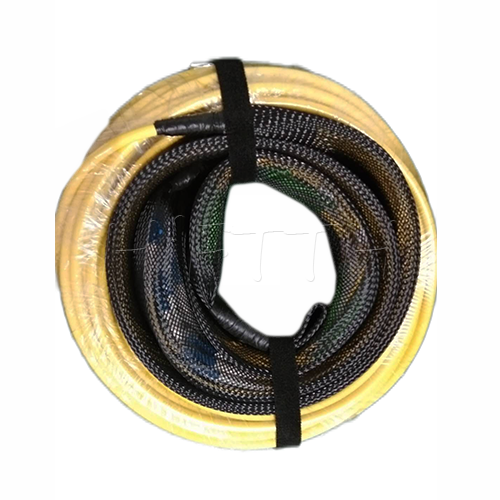






























More be coming
Outdoor Optical Fiber Patch Cord
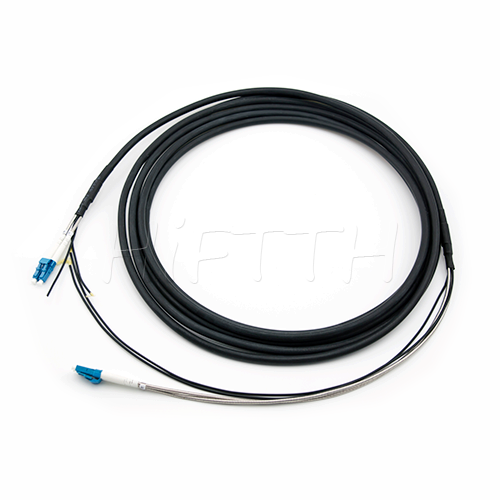
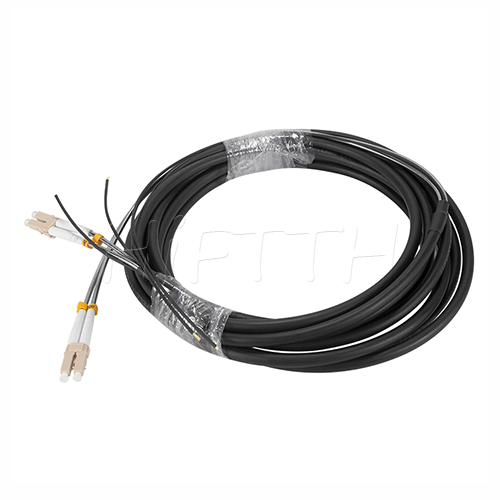
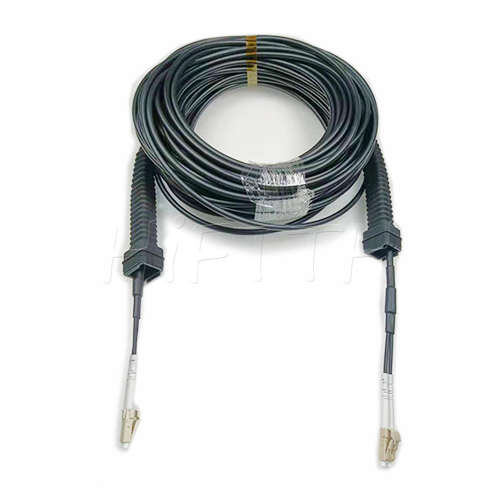
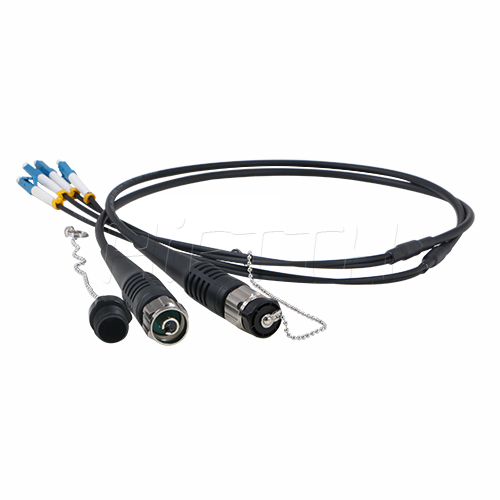
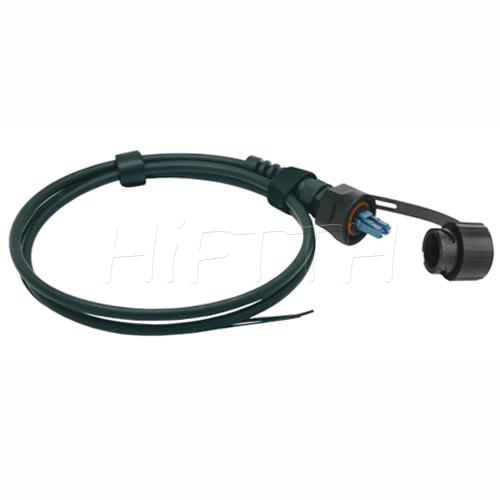
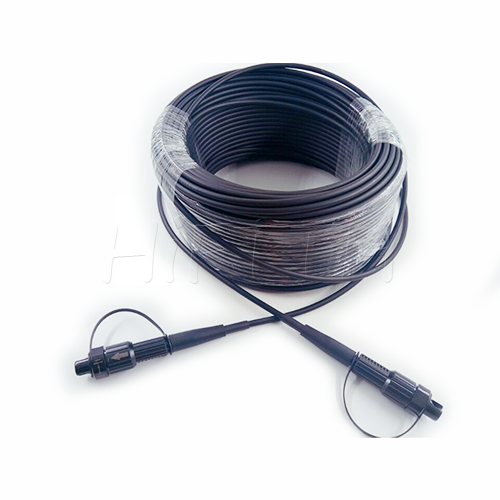
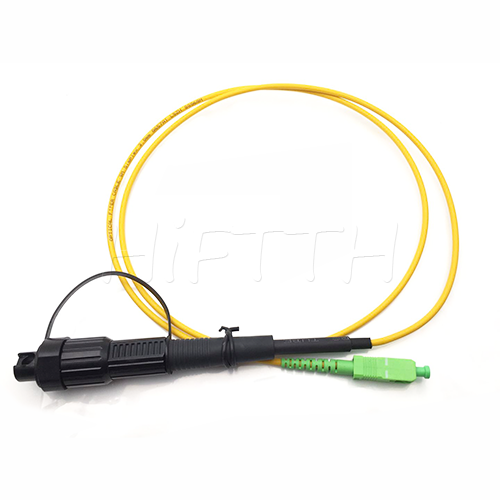
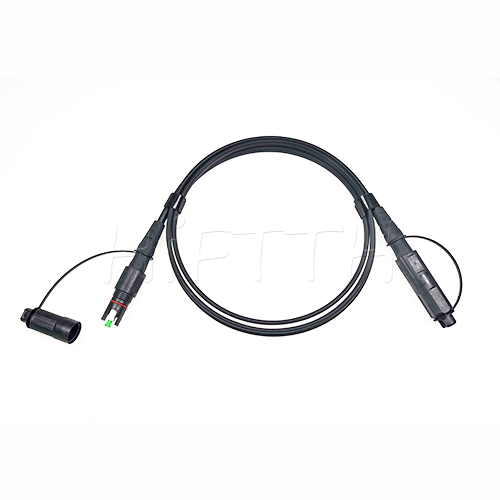
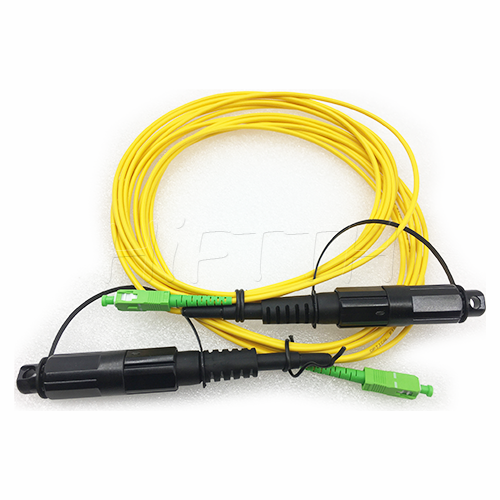
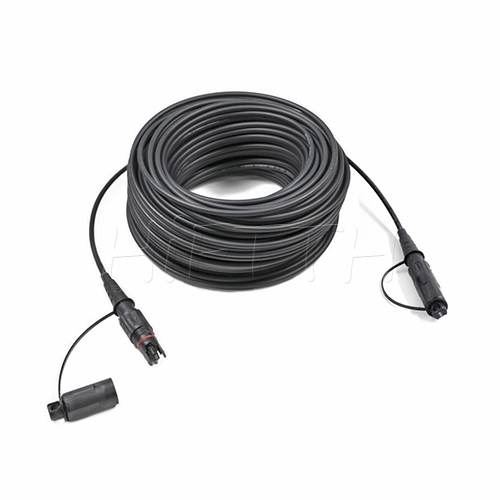
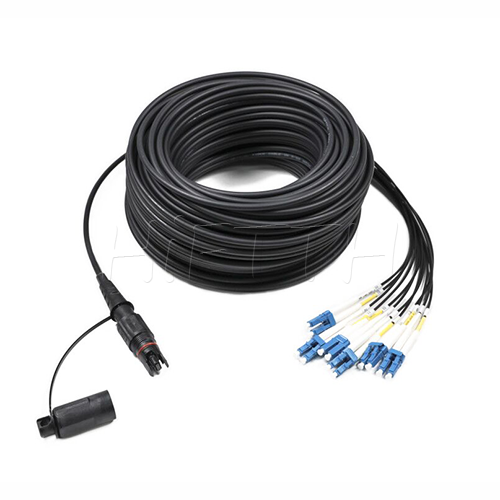













More be coming
MPO Optical Fiber Patch Cord
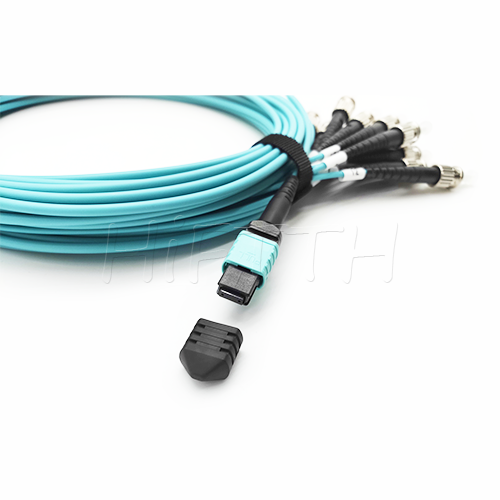
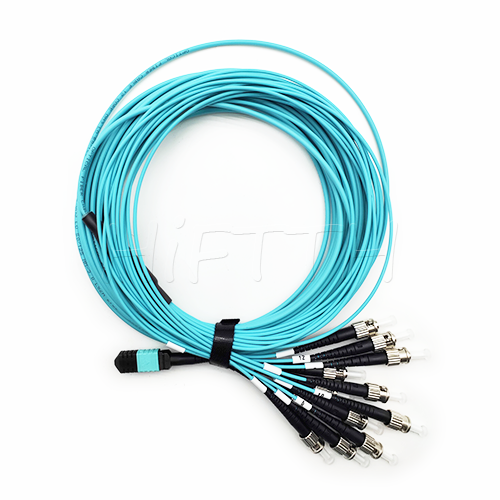
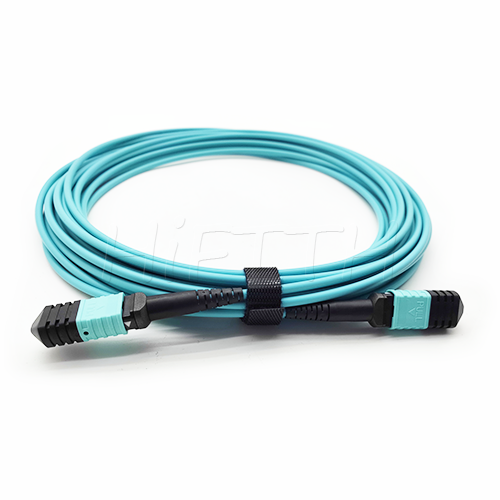
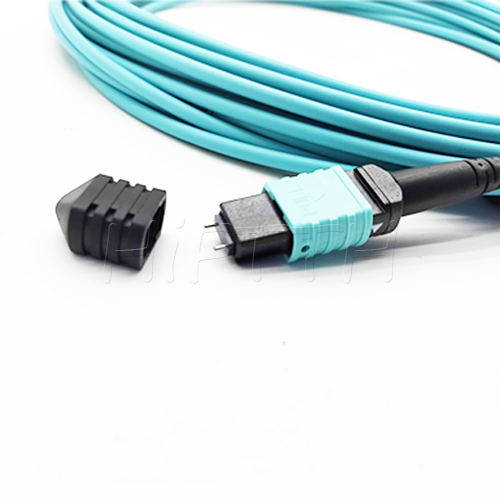
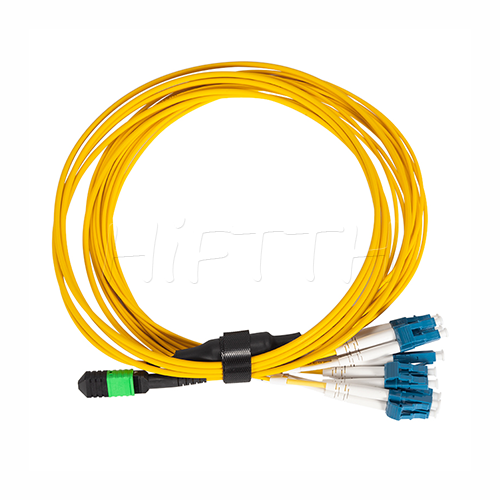
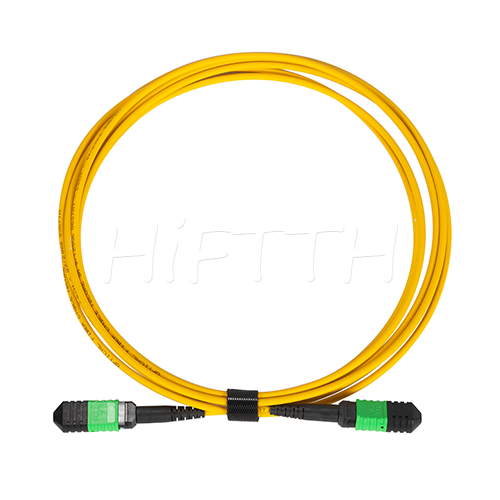
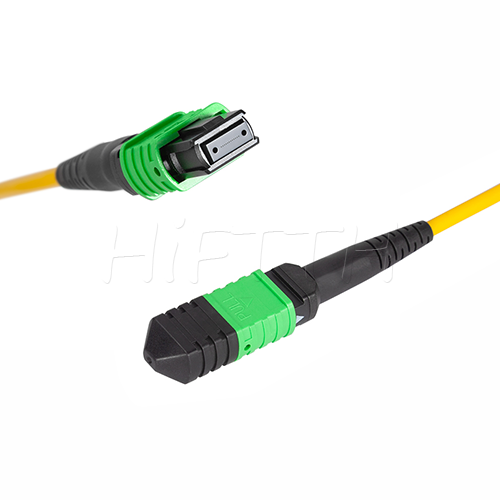
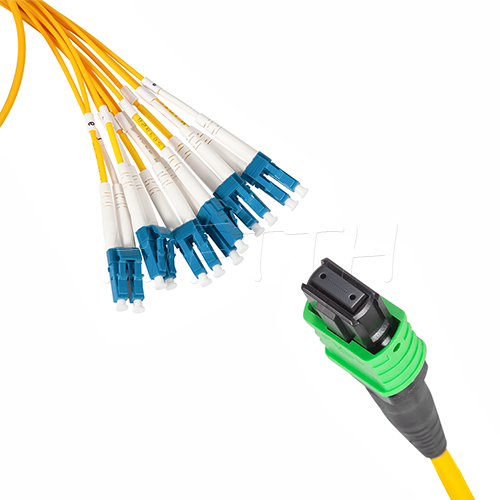
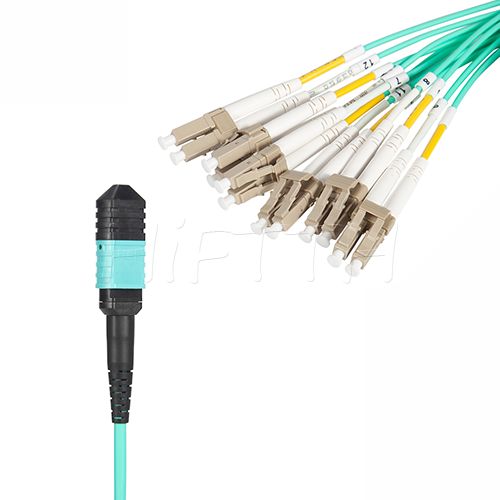
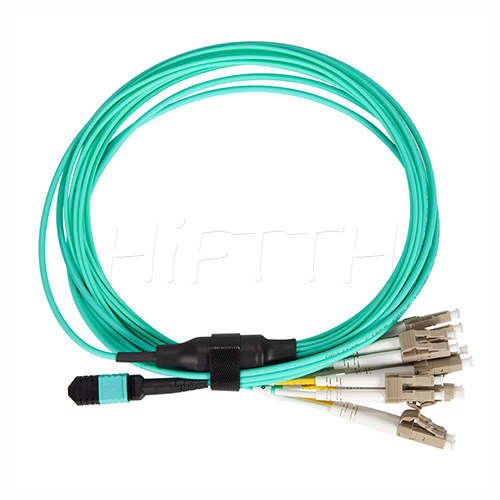
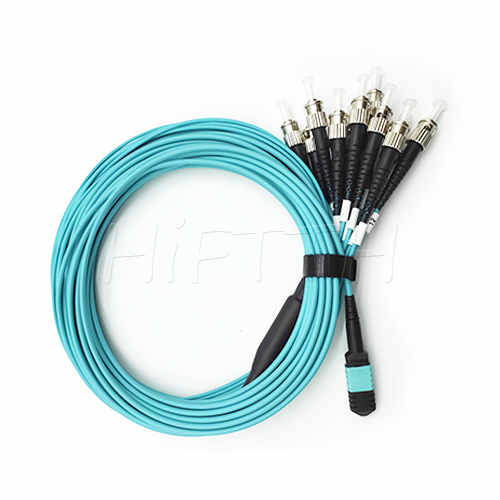
















More be coming
Fiber Pigtail
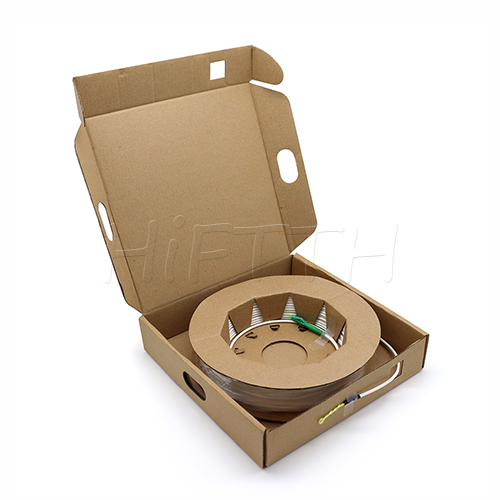
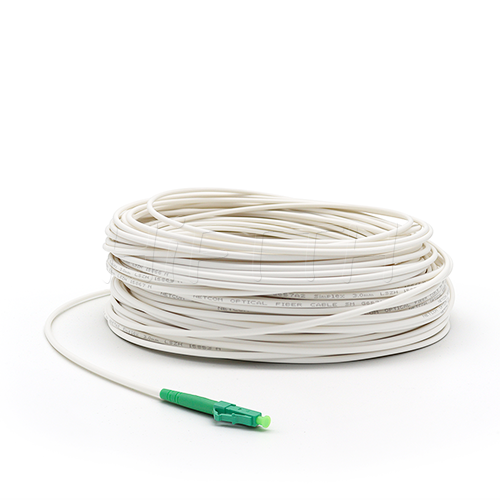
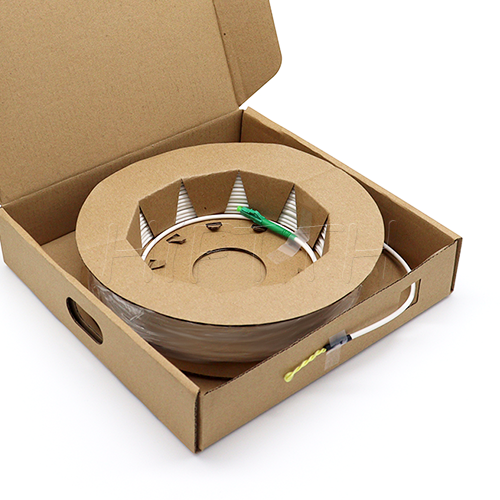
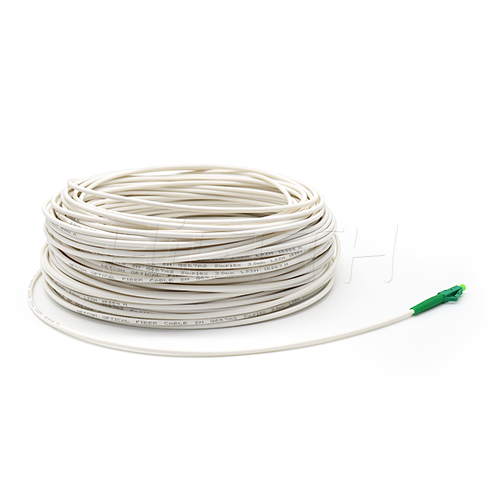
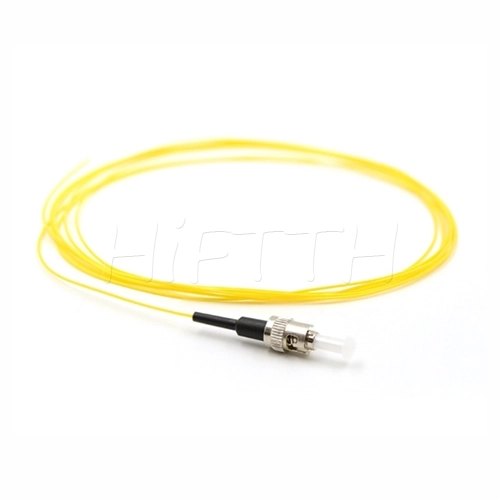
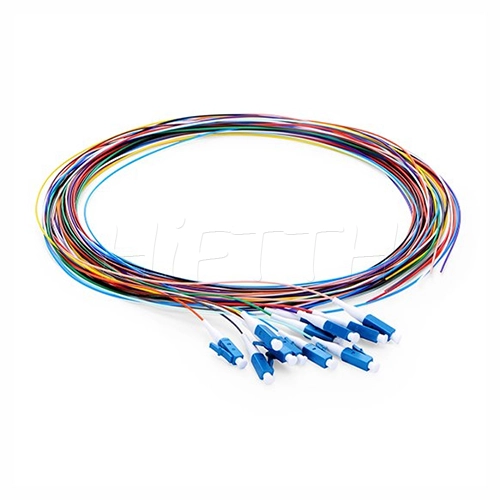
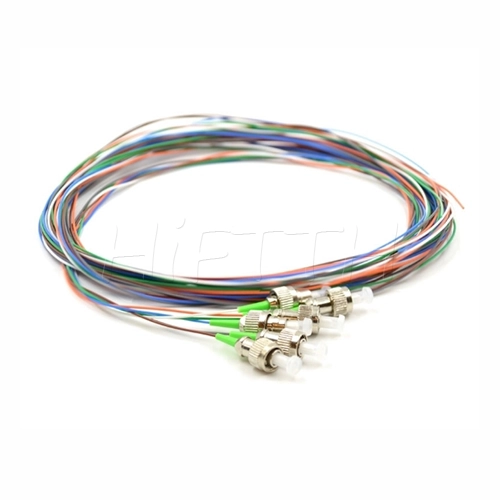
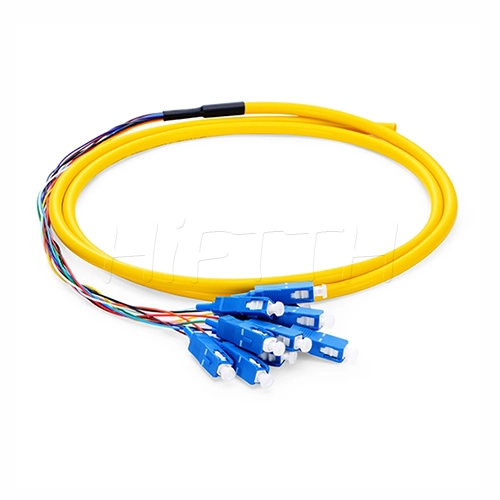
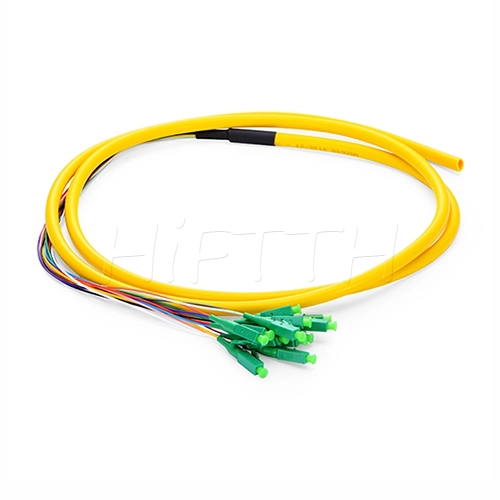
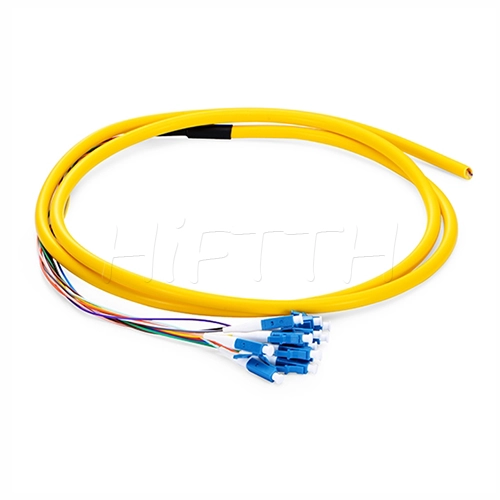
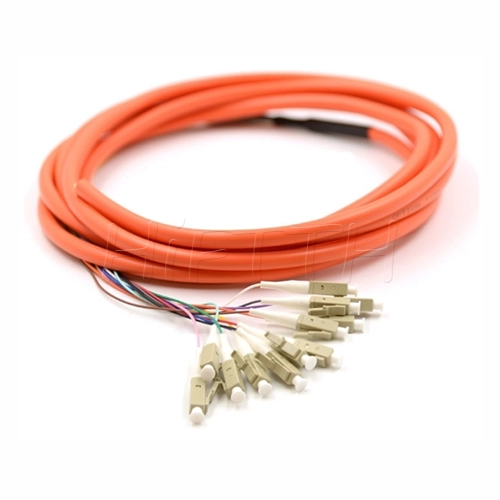
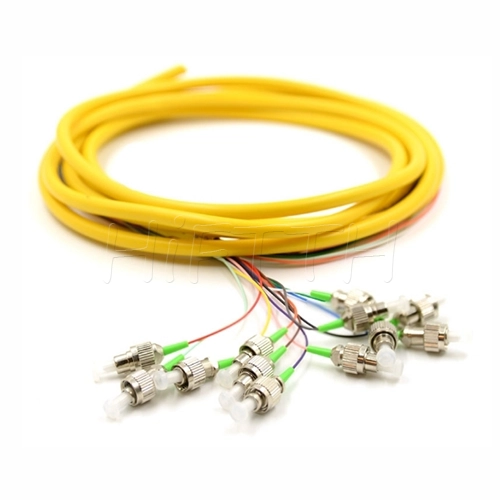
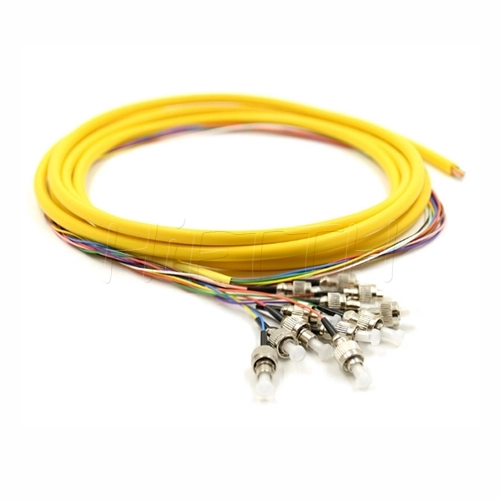































More be coming
You Ask
We Answer
Need help?
FAQs
What are the different types of optical fiber patch cords?
They are classified based on transmission medium (single-mode or multi-mode), connector types (e.g., FC, SC, ST, LC), and cable structure (simplex, duplex, or multi-fiber).
How do single-mode and multi-mode fiber patch cords differ?
Single-mode fibers have a smaller core diameter (typically 9μm) for long-distance transmission, while multi-mode fibers have larger cores (50μm or 62.5μm) suitable for shorter distances.
What connector types are available for fiber patch cords?
Common connectors include FC, SC, ST, LC, MTRJ, MPO, MU, SMA, FDDI, E2000, DIN4, and D4, each designed for specific applications.
What is the significance of APC, UPC, and PC connector polish types?
These polish types affect back reflection levels: APC connectors have an 8° angled polish for minimal reflection, UPC connectors have a flat polish with low reflection, and PC connectors have a slight curvature. The PC was instead by UPC now.
How does bend radius affect fiber patch cord performance?
Maintaining the specified minimum bend radius prevents signal loss and physical damage, ensuring optimal performance.
What are armored fiber patch cords?
Armored patch cords feature a protective stainless steel tube inside the outer jacket, enhancing durability and resistance to physical damage.
How should optical fiber patch cords be stored?
Store them in a clean, dry environment with controlled temperature and humidity to prevent damage and degradation.
What precautions should I take during cable splicing?
Always use a clean environment, ensure precise alignment, and avoid contamination to maintain low insertion loss.
What materials are used in the construction of optical fiber patch cords?
Optical fiber patch cords are constructed with a high-refractive-index core, a lower-refractive-index cladding, aramid yarns for strength, and a protective outer jacket.
How do I choose the right fiber patch cord for my application?
Consider factors such as transmission distance, required bandwidth, connector types, and environmental conditions to select the appropriate patch cord.
How do I ensure compatibility between different fiber patch cords and network equipment?
Ensure that the connector types, fiber modes (single-mode or multi-mode), and performance specifications match between the patch cords and equipment.
What testing is performed on fiber patch cords before deployment?
Tests include insertion loss, return loss, and end-face inspection to ensure they meet industry standards.
What is the maximum fiber capacity of this closure?
It can handle up to 576 fibers, depending on the splice tray configuration.
How do I select the appropriate outer jacket for a fiber optic patch cord?
Choose the outer jacket based on the installation environment: PVC is suitable for general indoor use, LSZH is ideal for areas requiring low smoke and zero halogen emissions, OFNP is designed for plenum spaces with strict fire codes, and armored jackets provide enhanced protection in high-traffic or hazardous areas.
How do I determine the appropriate length for a fiber optic patch cord?
Measure the exact distance between connection points, accounting for routing paths and slack for future adjustments, to ensure the patch cord is neither too short nor excessively long
What is the typical lead time for procuring fiber optic patch cords?
Lead times vary based on order size and customization; standard orders may ship within a few days, while bulk or custom orders could take more than a week.
Can different types of fiber optic connectors be interchanged?
Generally, connectors like LC, SC, ST, and FC are not interchangeable due to differing physical dimensions and locking mechanisms; using adapters is necessary to connect different types.
Is it possible to connect APC and UPC connectors directly?
Directly connecting APC (Angled Physical Contact) and UPC (Ultra Physical Contact) connectors is not recommended due to differing polish angles, which can lead to high insertion loss and reflection.
How do I choose between APC and UPC connectors for my application?
Base your choice on the application’s sensitivity to return loss: APC connectors are ideal for high-precision optical signal applications, while UPC connectors perform well in less sensitive systems.
Related Products
Your ODN network product assistant